Foreigners are tapping Chinese innovation to network and build businesses
China's innovations impress foreigners, change startup game, boost confidence
The consumption power of more than 1 million foreigners working or studying in China is disproportionately bigger than their tiny share (0.07 percent) of the total population - and whizzes of the country's homegrown tech ecosystem are sitting up and taking notice, as the economy transitions from export and investment-led growth to a consumption-driven model.
Manufacturers of gadgets, providers of technology-enabled services, and developers of intellectual property like innovative technologies are all vying to make life easier for the relatively small but monetarily significant foreigner community in China.
French engineer Sebastien Bernard, 37, will probably agree. He came to work and live in Beijing four months ago. The first thing he was asked to do by his friends and colleagues was to download and install WeChat, the all-in-one killer app, on his smartphone.
He complied, and his life is much the better for it, he said. As it transpired, Bernard was e-invited to join a WeChat group.
Initially, 15 foreigners chatted with each other and shared their life experiences on the e-group. Gradually, the group grew to a 200-member community of sorts that shared not just useful information like job links or party invitations but, wait for it, e-commerce discount coupons and weekend getaway packages.
Friendly advice sensitized Bernard to other treasures on WeChat. Among many other things, he learned to use the app to order food, book a taxi ride, buy movie tickets, and make digital payments for e-commerce.
Using Chinese apps, some of his friends even play online games, and borrow or lend money using e-credit channels that are redefining inclusive finance.
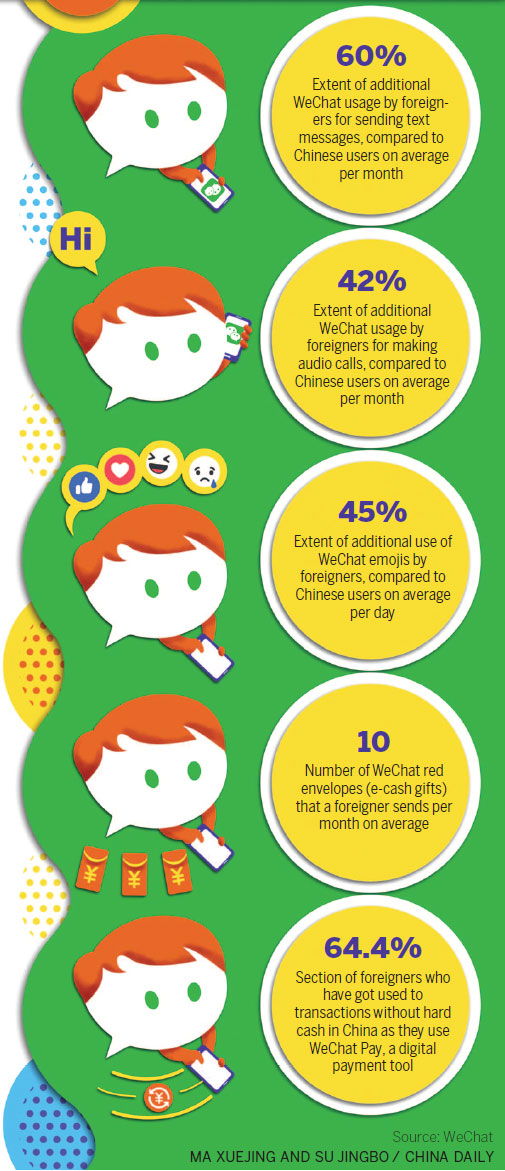
According to a WeChat report, by May 2017, foreigners in China sent 60 percent more WeChat messages than Chinese users on average per month. They also use WeChat audio calls 42 percent more than Chinese users.
Notably, foreigners in China are good at using different functions or features of WeChat. On average, they use emojis 45 percent more than Chinese users per day. Typically, a foreigner sends 10"red packets" - cash e-gifts - per month. Nearly 65 percent of foreigners who use WeChat use the app's digital payment tool WeChat Pay.
"Here in China, having WeChat and Alipay accounts is like being plugged into the world. The apps include almost every conceivable service that can help make modern life easy," said Bernard.
Agreed Yang Qiguang, 26, a researcher from Columbia University's Tow Center who is pursuing PhD at the Renmin University of China in Beijing.
"Chinese companies are creating a tech ecosystem that helps everyone, including foreigners, to work and live in a more convenient way."
Forming social networks using e-tools has become integral to modern life, particularly in urban areas - and China's tech ecosystem perhaps performs this function better than any other, by bundling consumption-related conveniences, he said.
"The tech ecosystem here facilitates people, including foreigners, to spend more. It is also boosting the confidence of both domestic and foreign companies operating in China. They know they now have powerful and reliable e-tools like apps to drive sales in a humongous market with more than 1 billion consumers," he said.
That's not all. Yang said China's tech ecosystem is fostering entrepreneurialism. Even foreigners living in China are beginning to use Chinese apps to start up in a variety of fields, including technology, education and entertainment. All this business activity is a long-term positive effect for the Chinese economy, he said.
Yang could well have been speaking about David Collier, 52, a Briton who has founded four startups so far, respectively in the United States, the United Kingdom and China.
Rikai Labs, his WeChat-based e-learning business in China, helps Chinese users to master the English language through proprietary automated software. Collier said every seven years, a big platform shift comes along - from web to mobile apps; from apps to messaging platforms - that creates huge opportunities.
"We chose to base our business on WeChat because it provides a great platform for a knowledge service. You have to build your business where people are spending their time, and the biggest messaging platform of all is WeChat," he said.
"Also, we can use WeChat payment for instant payment, QR codes for marketing purposes and to track user acquisition channels. Now with WeChat's mini programs, we can add interactive games and other features."
There's more. Links to Rikai Labs and related content can be shared socially online. "It provides a very compelling platform with real-time features, social distribution, marketing hooks and monetization," Collier said.
But risks abound too, he said. Platforms such as WeChat have become extremely competitive for startups. "If you don't move at high speed, riding with WeChat is like taking the maglev."
Data, however, suggest that foreigners appear to have an edge over Chinese users in exploiting the local tech ecosystem for small businesses and online social networking, which actually helps businesses directly or indirectly.
A case in point is Baopals, a startup founded by three expatriates. Call it the English Taobao, if you will. Baopals is anchored in Taobao and Tmall, the online shopping platforms owned by Alibaba Group, China's tech giant.

In July 2015, Charlie Erickson, Jay Thornhill and Tyler McNew, all US citizens in their late 20s and early 30s, developed Baopals, a website that helps translate product information on the Chinese Taobao and Tmall into English. In one stroke, the trio thus opened up the astonishing world of Chinese e-commerce, or 800 million products, to non-Chinese consumers in China.
Baopals already boasts 40,000 registered users, with 16,000 of them joining last year alone, doubling the user count in 2017. A Baopals user buys 58 items on average per year, and spends about 2,500 yuan ($368) to 3,500 yuan annually.
In addition to English, the website has Korean and Russian versions, making e-shopping simpler for foreigners in China.
The website is going from strength to strength on the back of the trio's innovations. It has introduced attractive sections like "The Cool, The Cheap& The Crazy". It accepts Alipay, WeChat Wallet and China UnionPay for payments.
Although e-commerce destinations are dime a dozen in China, most of them are in Chinese, and cater to Chinese consumers, so Baopals stands out, said Thornhill.
"Even on Amazon China, the default language is Chinese. When you switch to English, you still see lots of content in Chinese. They just haven't made the effort to serve China's expat population properly," he said.
That gap should spell business opportunities for those looking to start up, he said. "We are also changing the stereotype that Chinese goods are cheap products with low quality," he said, adding that several products including Xiaomi air purifiers and Huawei products are very popular among foreigners.
According to Thornhill, Baopals' revenue comes from service fee paid by shoppers. It charges a service fee of 5 percent of each item's price, plus a small fixed fee based on the item's price - 2 yuan for items priced below 30 yuan, and 8 yuan for items priced above 90 yuan. More than 2.3 million products had been sold by Jan 17 this year, a huge increase from the same period last year.
Given the experience in China, it is clear that homegrown technologies can succeed outside the mainland, he said. "This year is going to be a big year for Baopals, as we'll be launching our global service. Expats leaving China can continue buying things they love here, and foreigners everywhere can discover the treasures of China's online shopping."
Agreed Yang from the Tow Center. China's tech ecosystem, he said, provides foreigners on the mainland with well-rounded platforms to do business not only in China but across the world.
"It may take years for foreigners to build such infrastructure themselves. The time and energy saved during the process can be used for bolstering their own products and business."
It's not just small players such as Baopals that are drawing confidence from their success in China. Even e-payment giants such as WeChat Pay and Alipay, emboldened by their rapid adoption among foreigners in China, are confident of replicating their success worldwide.
Alipay has introduced its payment services, including departure tax refunds, at 10 major international airports in Japan, Thailand and New Zealand. Although the initial goal is to serve Chinese tourists traveling overseas, the larger plan is to roll out Chinese technologies worldwide and gain a global visibility and footprint.
So, it has struck cooperation agreements with local banks and companies in foreign markets, to provide e-payment services. For instance, its partners in Japan are Hida Credit Union and Kyoto Shinkin Bank, which helps attract Japanese users as well. Using such strategies, Alipay has accumulated more than 1 billion users in all, including 300 million outside China.
Sources: China Daily/Asian News Network
Related posts:
Reuters pic. The term 5G stands for a
fifth generation — to succeed the current fourth generation of mobile
connectivity that has made...


















 Alibaba, China’s eCommerce giant, has quickly come onto everyone’s radar as it presents the possibility of being the largest tech IPO ever. According to the New York Times, the company is expected to go on the market at a value of roughly $200 billion – larger than US tech companies Amazon, eBay or Facebook. This week, we bring you articles to explain who Alibaba is and what you can expect from them in the future.
Alibaba, China’s eCommerce giant, has quickly come onto everyone’s radar as it presents the possibility of being the largest tech IPO ever. According to the New York Times, the company is expected to go on the market at a value of roughly $200 billion – larger than US tech companies Amazon, eBay or Facebook. This week, we bring you articles to explain who Alibaba is and what you can expect from them in the future.